|


| |
UCY ENERGY supplies coal and coke in
industrial and wholesale quantities physically
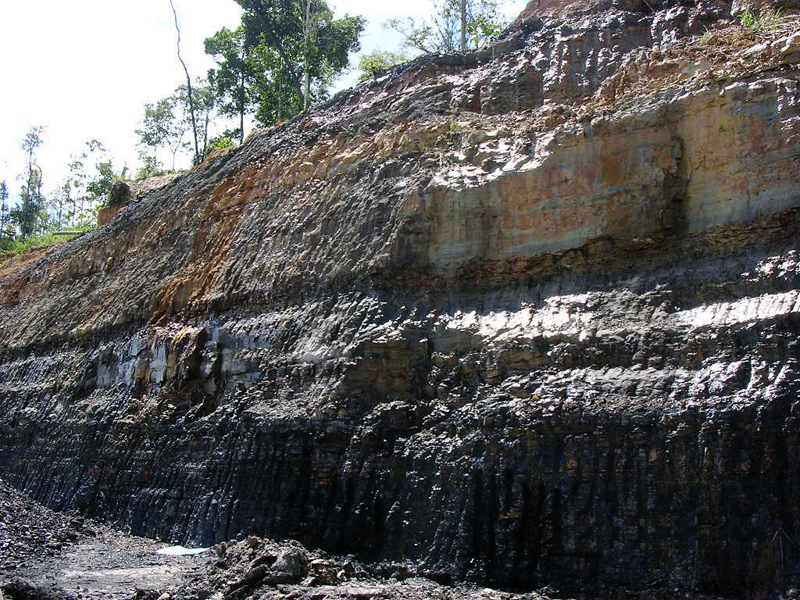
Coal is a readily combustible black or
brownish-black sedimentary rock normally occurring in rock strata in layers or
veins called coal beds. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be
regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature
and pressure. It is composed primarily of carbon along with variable quantities
of other elements, chiefly sulfur, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
Coal begins as layers of plant matter accumulate at the bottom of a body of
water. For the process to continue the plant matter must be protected from
biodegradation and oxidization, usually by mud or acidic water. The wide shallow
seas of the Carboniferous period provided such conditions. This trapped
atmospheric carbon in the ground in immense peat bogs that eventually were
covered over and deeply buried by sediments under which they metamorphosed into
coal. Over time, the chemical and physical properties of the plant remains (believed
to mainly have been fern-like species antedating more modern plant and tree
species) were changed by geological action to create a solid material.
Coal, a fossil fuel, is the largest source of energy for the generation of
electricity worldwide, as well as one of the largest worldwide anthropogenic
sources of carbon dioxide emissions. Gross carbon dioxide emissions from coal
usage are slightly more than those from petroleum and about double the amount
from natural gas. Coal is extracted from the ground by mining, either
underground or in open pits.


|